Part 8. Units and Conversions
Metric is the most common form of measurement used worldwide and is based on a system of tenths. For example, the Meter is the metric standard for length and one tenth of a meter is a decimeter. One hundredth of a meter is a centimeter, one thousandth of a meter is a millimeter and one thousand meters is a kilometer. The same convention applies to most metric standards: For example, the Gram, Decigram, Centigram, Milligram, and the Liter, Deciliter, Centiliter, and Milliliter.
The imperial system is an older system of measurement that does not use standard conventions. Imperial units include inches, feet, pounds, ounces and gallons. Imperial units are very common in the United States and North America, but less common globally. In the injection molding industry, the inch is the most commonly used imperial unit of measurement for length. Twelve inches equal a foot, three feet equal a yard, and one thousand, seven hundred sixty yards equals a mile.
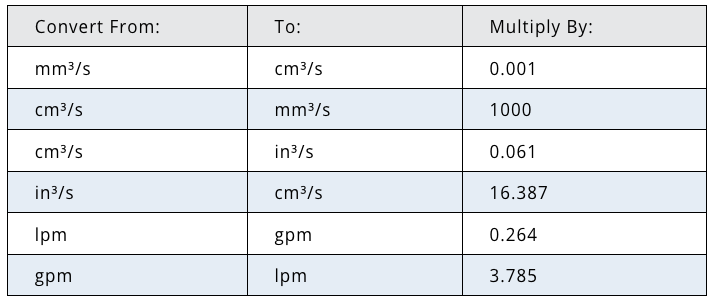
Imperial units can also become somewhat confusing when deal-ing with weight and volume measurements. For example, sixteen ounces in weight equals one pound, while one hundred twenty-eight fluid ounces equals a gallon. Since most injection molding facilities operate globally, it is common for personnel to convert measure-ments from metric units to imperial units, and vice versa, on a regular basis.